
Even little fibs can have serious consequences — and some of them just might surprise you
Most of us have told a lie at one time or another. Some lies are harmful. Others, like small fibs to avoid hurting someone’s feelings, are mostly harmless. Some lies are even intended to protect others. But no matter the type of lie, it takes a surprising amount of brainpower to pull it off, which can be costly.
Lying requires significant mental effort. Imagine you’re late to class and decide to lie about why. You might say, “I had to stop by the library and pick up a book.” When your teacher asks, “The book I assigned last week?” you must quickly decide how to respond. You may say, “No, it was a different book,” and now you have to be ready with another title. This constant mental juggling uses up brainpower that could be spent on more important tasks.
A lot of this mental work is done in the prefrontal cortex, the part of the brain responsible for working memory, planning, problem-solving, and self-control. Using these resources for lying means they are not available for other tasks, like solving math problems or remembering important facts.
Lying also has social consequences. People generally value honesty and don’t like liars. If people view you as untrustworthy, it can damage your relationships. Even well-intended lies, such as insincere compliments, can backfire. If your friends realize they can’t trust your compliments, those compliments become meaningless.
Most people don’t lie very much, says Timothy Levine, a psychologist at the University of Alabama at Birmingham who studies deception. His research shows that almost three-quarters of people rarely lie, and 90 percent of the lies they tell are “white lies.” However, Levine’s research also shows that while most people don’t lie often, a few lie a lot. The top one percent of liars, according to Levine, tell more than 15 lies per day. Some chronic liars are insecure. Others may lie about their accomplishments because they’re conceited or overly impressed with themselves. Still others lie to take advantage of people — perhaps even to cheat them or to steal from them.
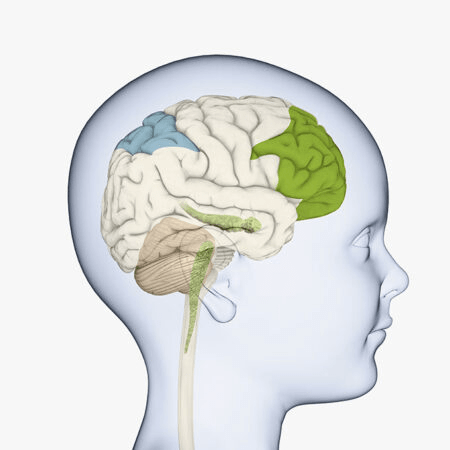
The brain’s prefrontal cortex, behind the forehead (shown right, in darker green) isn’t fully mature until we are in our 20s. That’s a problem for adolescents. This part of the brain helps us understand risk. It’s also in charge of a lot of our higher-level thinking, such as planning and self-control.
DORLING KINDERSLEY/GETTY IMAGES PLUS
Lying is especially hard for young people because their prefrontal cortex is not fully developed until around age 25. This part of the brain helps with higher-level thinking, such as planning and self-control. When it’s busy with tasks related to lying, it has a harder time doing other important tasks.
Some lies never stop, like those told by spies or people hiding a difficult home life. Pretending to be something you’re not almost every hour of every day is mentally draining and can have long-lasting effects. Over time, this kind of lying uses up the brain resources needed for thinking and planning.
Most people value honesty, and research shows that honest people build social capital, or goodwill, within their communities. Trust is essential for healthy relationships and a well-functioning society.
Lying may seem easier in the short term, but it has significant cognitive and social costs. By striving to be honest, we can save mental energy and build stronger, more trusting relationships.
Neil Garrett, a neuroscientist at the University of East Anglia in Norwich, England, has studied how emotions affect our willingness to be dishonest. He points to a study where students were given a beta blocker, a medicine that dampens emotions. These students were more likely to cheat on an exam than those who didn’t receive the medicine, possibly because they felt less fear or anxiety about being dishonest.
Garrett and his team also examined the relationship between lying and activity in the amygdala, the part of the brain that processes emotions. They conducted an experiment where volunteers played a game to make money by lying to a partner. Brain scans showed that the amygdala was very active when participants first lied. However, as they continued to lie, activity in the amygdala decreased, and the participants lied even more. These findings were reported in Nature Neuroscience.
Garrett suggests this brain effect might be similar to how our sense of smell adapts to strong odors. Initially, a strong smell is overwhelming, but after a while, we barely notice it. Emotions might work similarly; the more you lie, the less you feel the uncomfortable emotions like fear or guilt. In other words, lying becomes easier the more you do it.
Nearly all cultures value honesty, notes Victoria Talwar, a psychologist at McGill University in Montreal, Quebec. She suggests that creating a culture that reinforces the value of honesty can help. One strategy is to support friends while still being truthful. “When people’s friends are truthful with them,” she says, “it creates a culture of honesty among them,” which builds stronger friendships.
Jennifer Vendemia, a neuroscientist at the University of South Carolina, emphasizes that lying lessens when there are consequences for dishonesty. However, she adds that rewarding truth-telling is more effective than punishing lying. This is especially important when people share significant truths about themselves. “Being able to tell the truth to a friend is rewarding,” she says. “It feels good.”
Most people know that lying is generally bad and can have serious consequences. Science is now revealing how dishonesty impacts the brain and undermines the trust essential for strong relationships.
Link: https://peacelilysite.com/2024/06/13/the-science-of-lying-its-cognitive-and-social-costs/
Source: Lying won’t stretch your nose, but it will steal some brainpower by Avery Elizabeth Hurt
https://www.snexplores.org/article/lying-brain-power-prefrontal-cortex-truth-telling