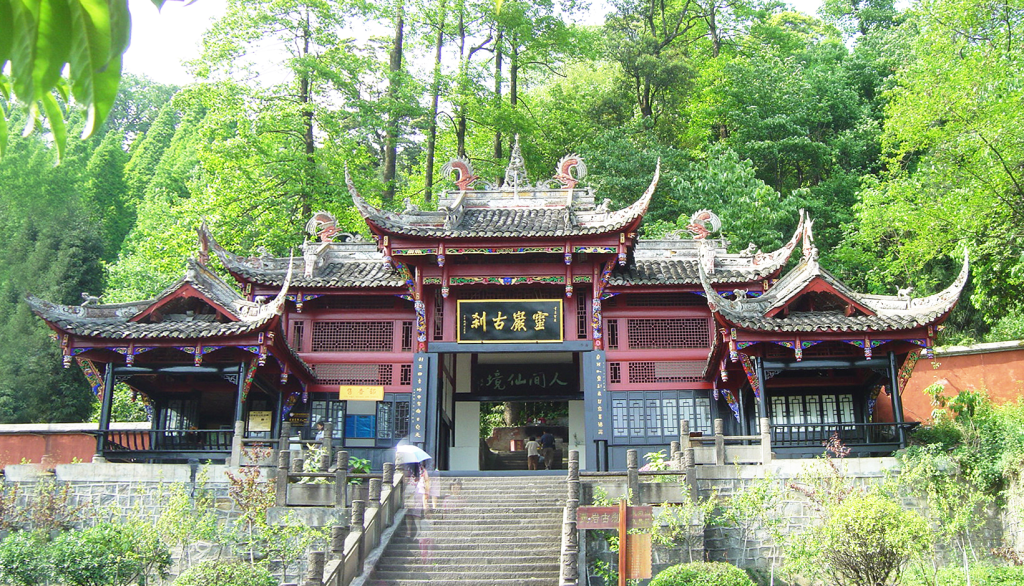
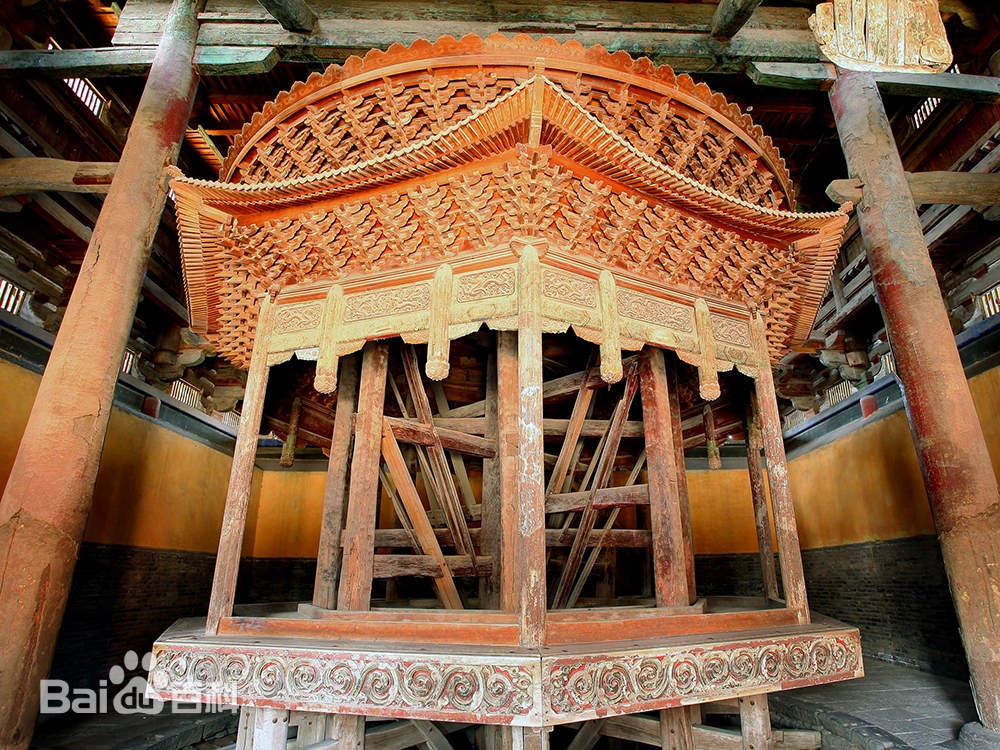
Located in the northwest of Mount Tai, Lingyan Temple was founded during the Eastern Jin Dynasty and boasts a history of over 1,600 years. It is regarded as one of the most important sacred sites of Chinese Buddhist culture. Since the Tang Dynasty, Lingyan Temple has enjoyed great renown, and together with Qixia Temple in Nanjing, Guoqing Temple on Mount Tiantai in Zhejiang, and Yuquan Temple in Dangyang, Hubei, it has been hailed as one of the “Four Great Temples of China.” The eminent monk Tang Xuanzang once resided here to translate Buddhist scriptures. From Emperor Gaozong of Tang onward, many emperors stopped to worship at this temple on their way to perform imperial rites at Mount Tai, a testament to its revered historical status.
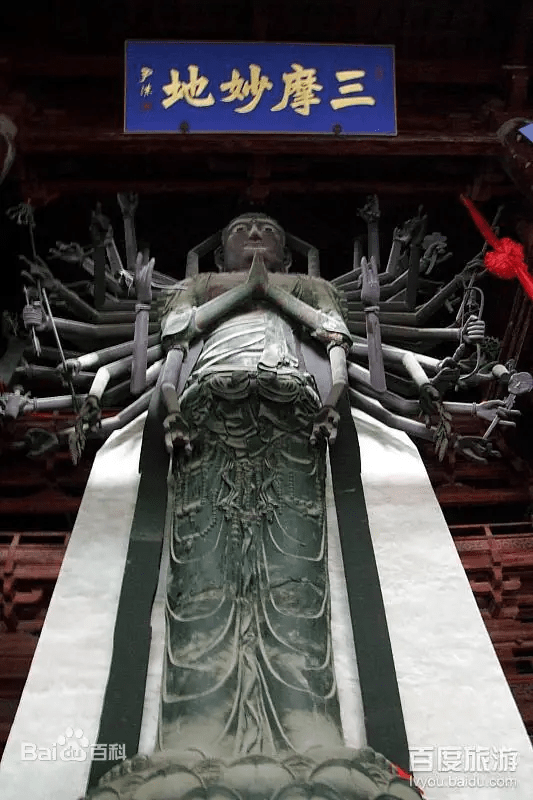
Although I personally prefer the majestic beauty of untouched natural landscapes, I was deeply moved by the profound cultural and religious artistry of Lingyan Temple. Within the temple grounds, ancient trees such as Chinese wingnut, cypress, and banyan rise skyward, creating a tranquil and sacred atmosphere. As an integral part of the World Natural and Cultural Heritage site of Mount Tai, Lingyan Temple is especially renowned for its colored clay sculptures of Arhats, which hold a prominent place in the history of Chinese sculpture.
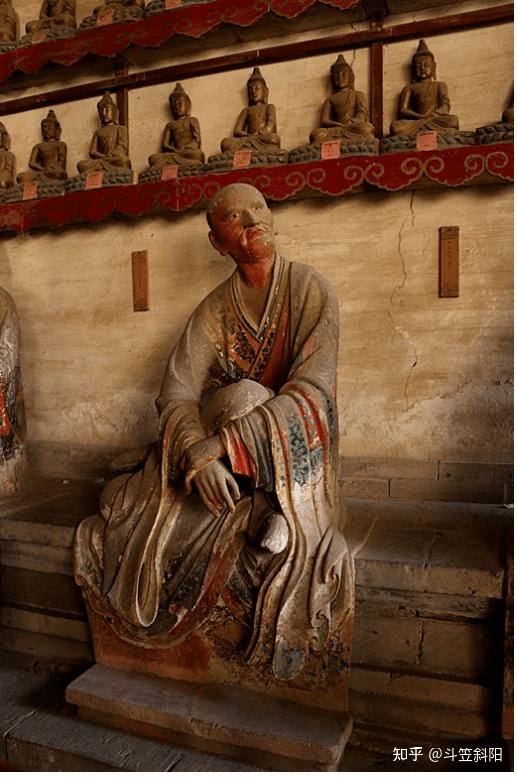
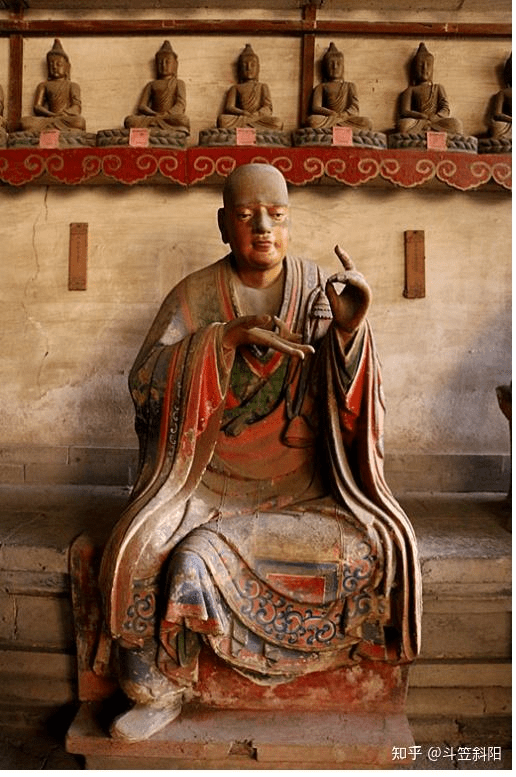
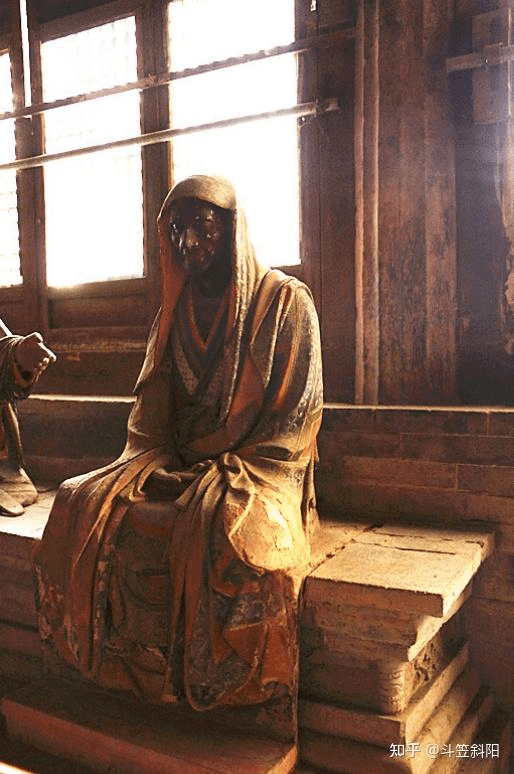
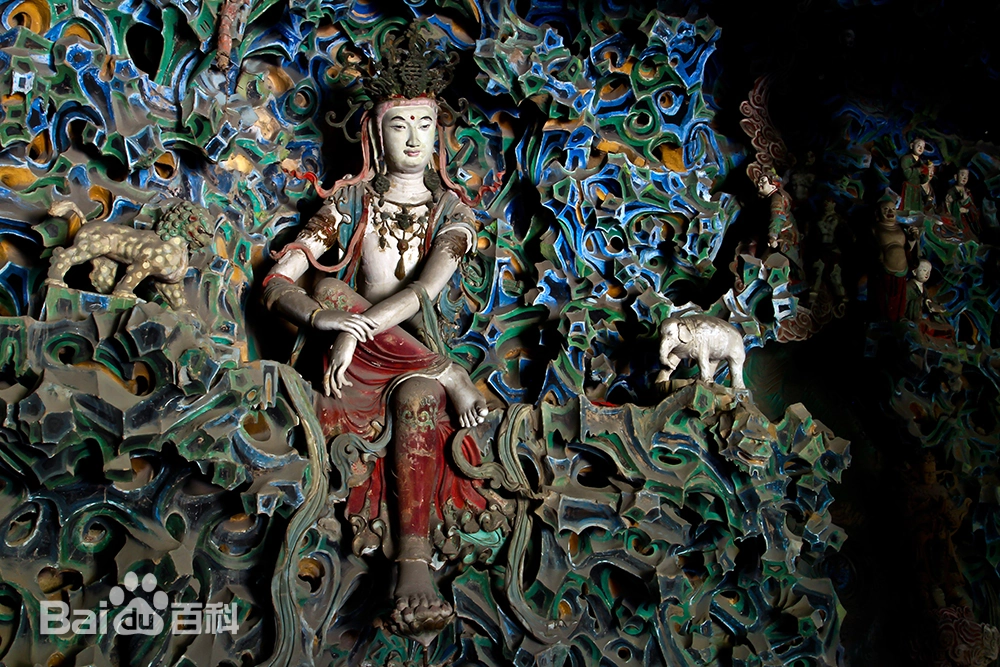
Stepping into the solemn Thousand Buddha Hall, one is struck by the breathtaking sight of the Arhat statues—40 lifelike clay figures arranged in a semicircle along the inner walls. Among them, 29 represent disciples of Shakyamuni and Indian masters such as Bodhidharma and Kumarajiva. The remaining 11 depict eminent Chinese monks, including Huiyuan, Huike, Huichong, and various abbots of Lingyan Temple. According to inscriptions and scholarly research, the original set consisted of 32 statues, first created in the third year of the Zhiping reign of Emperor Yingzong of the Song Dynasty (1066). Additional painting and sculpting were done in the first year of the Zhiyuan reign (1328) during the Yuan Dynasty. The Thousand Buddha Hall was renovated in the 15th year of the Wanli reign (1587) in the Ming Dynasty, at which time the number of Arhats was increased to 40. The final touch-up was completed in the 13th year of the Tongzhi reign (1874) of the Qing Dynasty.
Each statue stands about 1.6 meters tall and is seated on a waist-high brick pedestal roughly 80 centimeters in height, with the top of each statue rising 105 to 110 centimeters above the seat. The overall sculptural style is remarkably realistic, emphasizing the individuality and inner spirit of each figure: square faces, prominent noses, distinct facial features, and dynamic, textured robe patterns. The ancient artisans broke away from conventional, stylized Buddhist iconography and instead grounded their work in real life, endowing each Arhat with unique expressions and postures—some sit in meditation, others clasp their hands or hold staffs; some appear ragged and emaciated, while others exude noble dignity and elegance. Each figure is infused with spirit and personality, appearing almost alive, as if they might speak or move at any moment.
What’s even more astonishing is the meticulous attention to detail in both facial expressions and bodily movement, as well as the relationship between the robes and the human form. The flowing lines of the garments, the way the folds respond to motion, and the tactile quality of the fabric all reflect a masterful understanding of form and rhythm. One medical expert even remarked that, “Through the Arhats’ robes, one can perceive the ancients’ precise grasp of human anatomy.”
The Arhat sculptures at Lingyan Temple are not only masterpieces of religious art but also represent the pinnacle of ancient Chinese realistic sculpture. The renowned scholar Liang Qichao once visited the site and inscribed a stone tablet calling them “The finest sculptures in the land.” Famed art master Liu Haisu also praised them, writing: “The Arhats of Lingyan—first under heaven—vivid and lifelike, with flesh and spirit.”
Lingyan Temple is more than a place of worship—it is a living chronicle of Buddhist heritage carved from clay and shaped by the hands of genius. Whether you are a devout practitioner, a history enthusiast, or an art lover, a visit to Lingyan Temple will surely leave you moved by its rich cultural legacy and breathtaking artistic beauty.