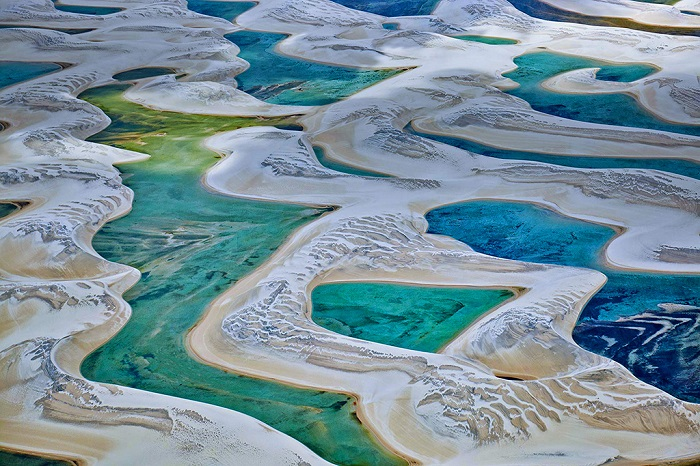
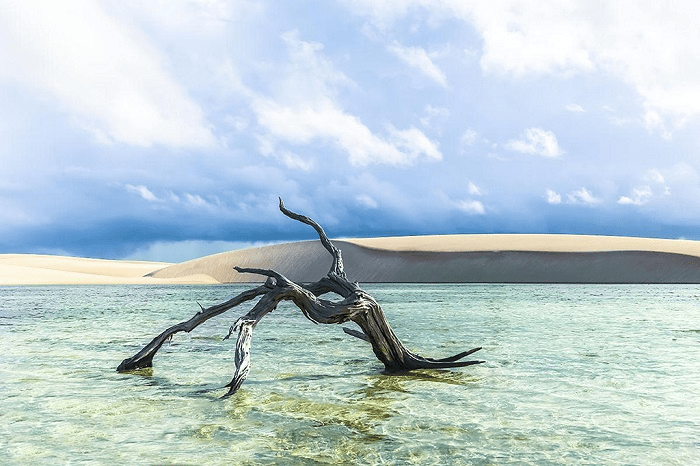
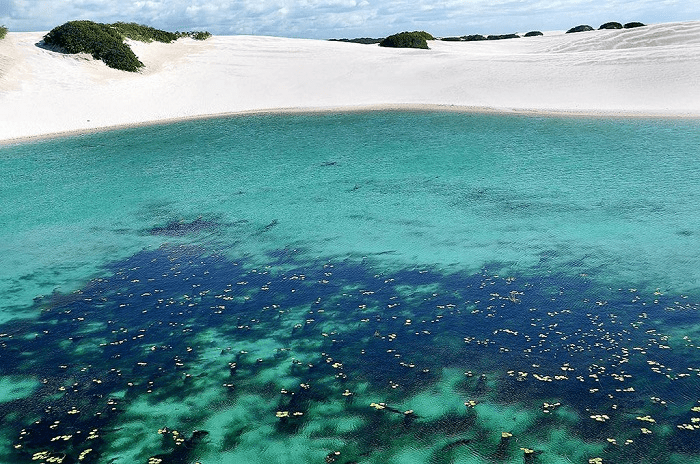
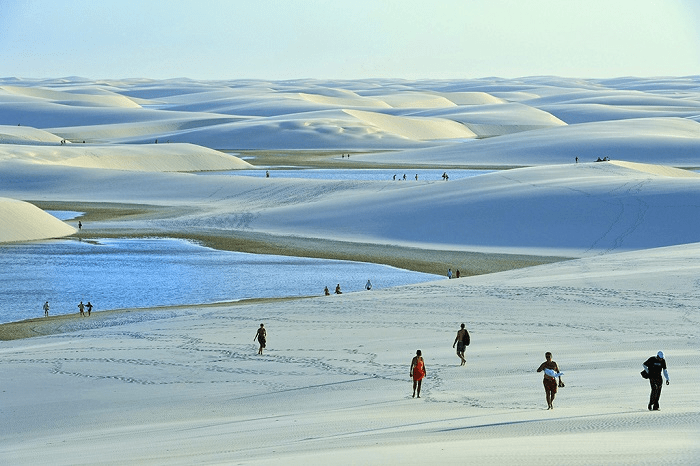
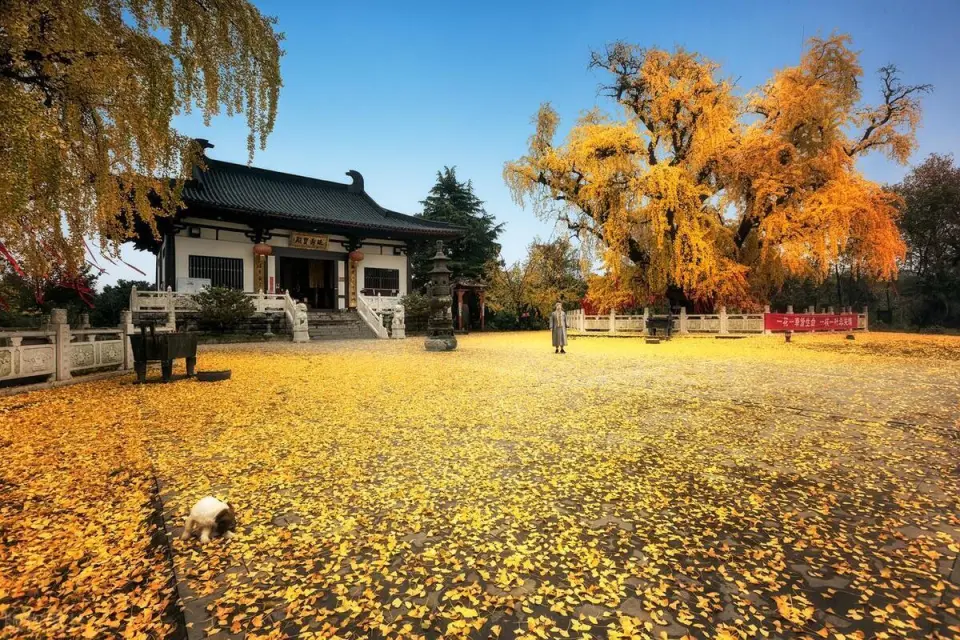
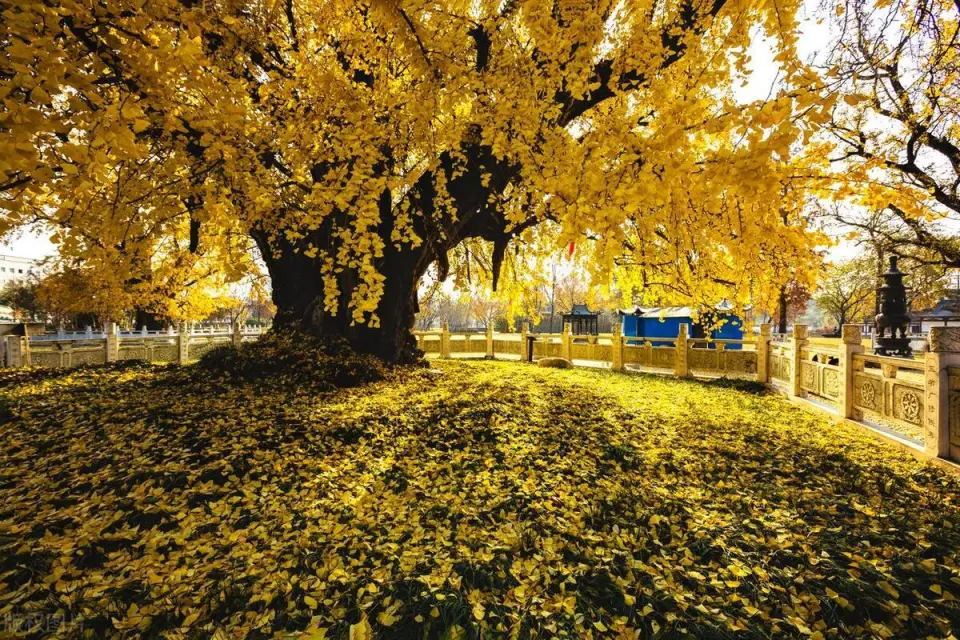
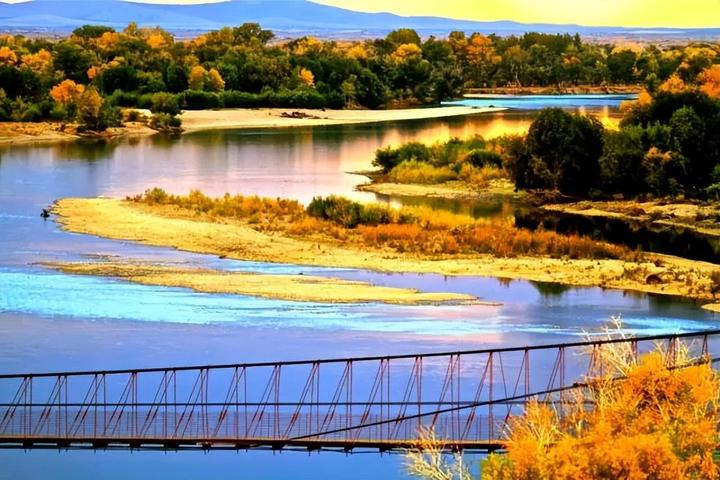
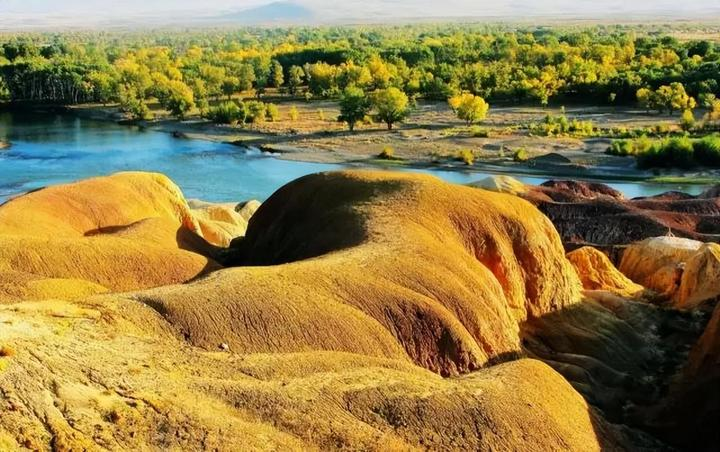
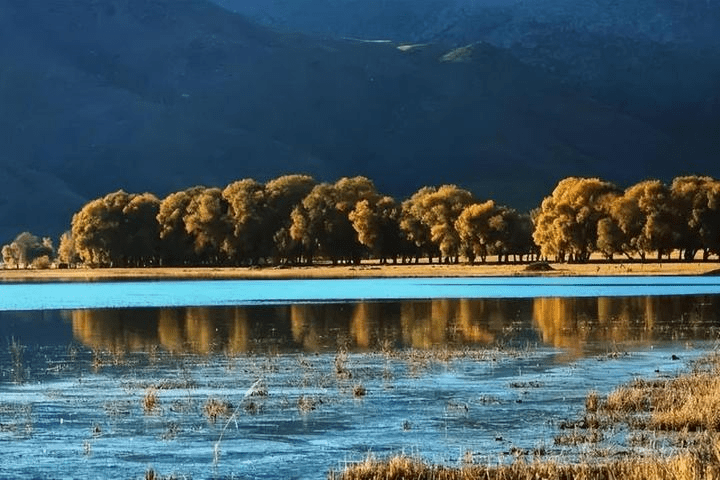
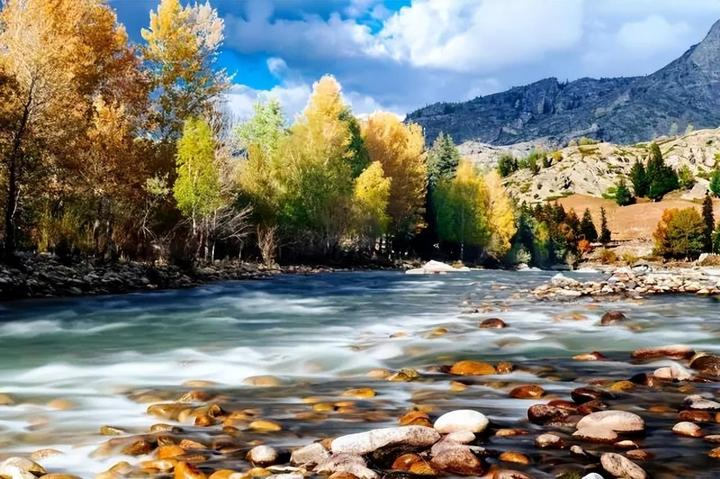
As autumn quietly arrives on the vast land of Xinjiang, a stunning visual feast also begins. Autumn in Xinjiang is like a vivid, colorful painting, with every scene exuding its own unique charm.
If Tibet offers people a spiritual shock, then Xinjiang provides a visual impact.
This is the place in China where autumn’s colors are the richest, with vibrant hues blooming amidst alternating poplar forests, lakes, rivers, and deserts.
If you missed the lush greenery of summer, you definitely cannot miss the splendid autumn of Xinjiang. Below is a suggested itinerary for Northern Xinjiang.
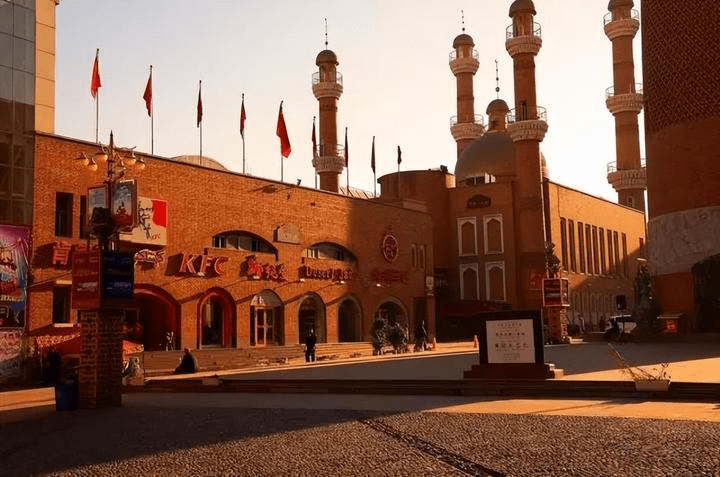
Day 1: Arrive in Urumqi, which can be reached via Urumqi International Airport. Upon arrival, explore the city with key places such as the Erdaoqiao International Bazaar, Hongshan Park, and the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Museum.
The International Bazaar is the largest bazaar in the world, combining Islamic culture, architecture, ethnic commerce, entertainment, and dining. It is known as the “Window to Xinjiang,” “Window to Central Asia,” and “Window to the World.” It symbolizes the prosperity of commerce and tourism in Xinjiang and serves as a scenic landmark in Urumqi, a city rich in ethnic diversity.
The architecture reflects a strong Islamic style, and while fulfilling modern functionality, it also recreates the historical glory of the ancient Silk Road. The bazaar showcases the deep ethnic characteristics and regional culture of Western China.
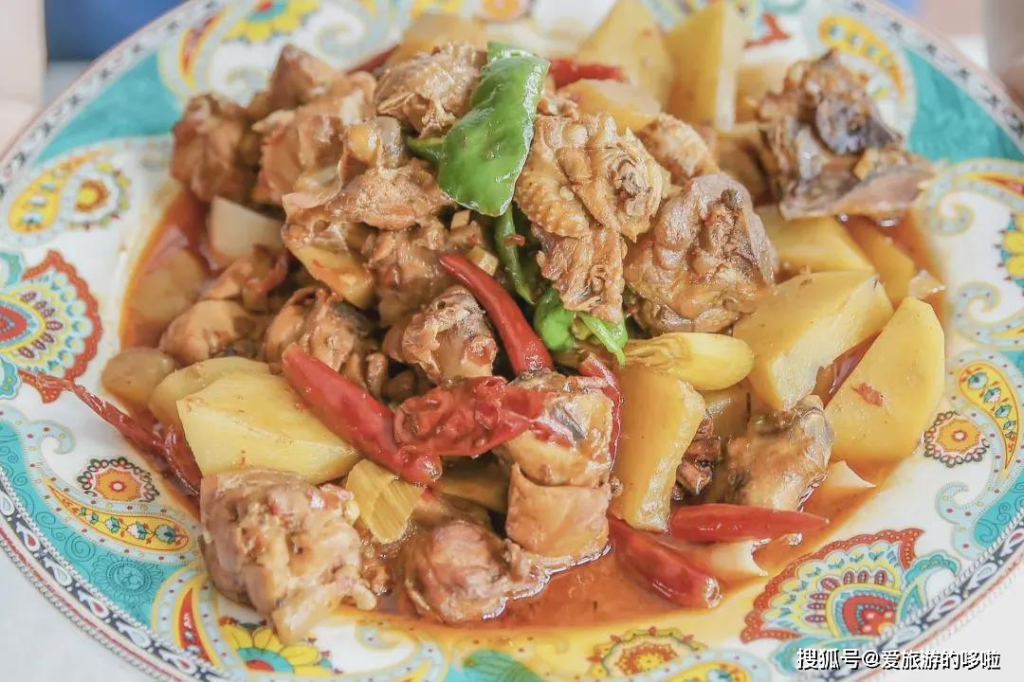
You can take Urumqi’s city rapid bus or BRT line 3 and get off at Erdaoqiao Station.Try Big Plate Chicken, baked buns, lamb kebabs, and hand-pulled rice to ignite your taste buds.
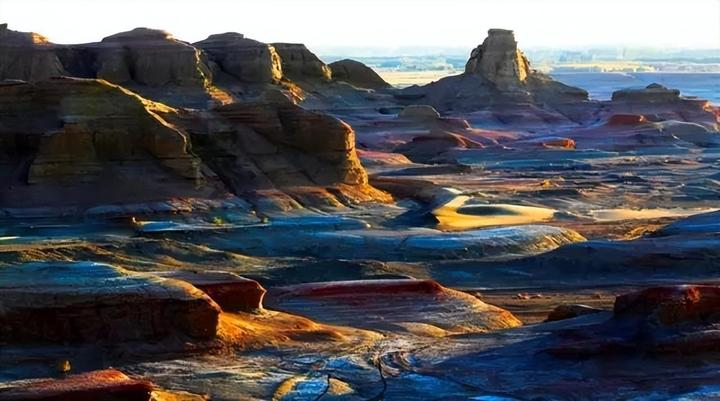
Day 2: Urumqi to Urho Ghost City, exploring the wind-eroded landscapes. Ghost City is also known as Urho Wind City.
It is a unique wind-eroded landform with bizarre shapes. The local Mongolian people call this place “Sulumuhaque,” and the Uygur people refer to it as “Shaytankarshi,” which means Ghost City. The Ghost City stands like a mighty castle in the vast Gobi desert.
This castle-like formation resembles pavilions, towers, corridors, streets, and even a demon’s treasure hall. On the western side of the city gate, there is a rock formation called the “Stone Monkey Gazing at the Sea,” and within the city, you’ll find the towering “Mount Fuji,” the temple-strewn “Angkor Wat,” the magnificent “Potala Palace,” and shapes that resemble a cobra, a roc, and other creatures. These scenes are incredibly varied and dazzling, forming a dreamlike maze.
From a distance, you’ll marvel at its grandeur and magnificence, praising nature’s incredible craftsmanship. Bathed in the glow of the setting sun, the Ghost City becomes a kaleidoscope of colors, resembling a medieval castle with uneven heights and intricate layers, creating a unique spectacle in the Gobi desert.
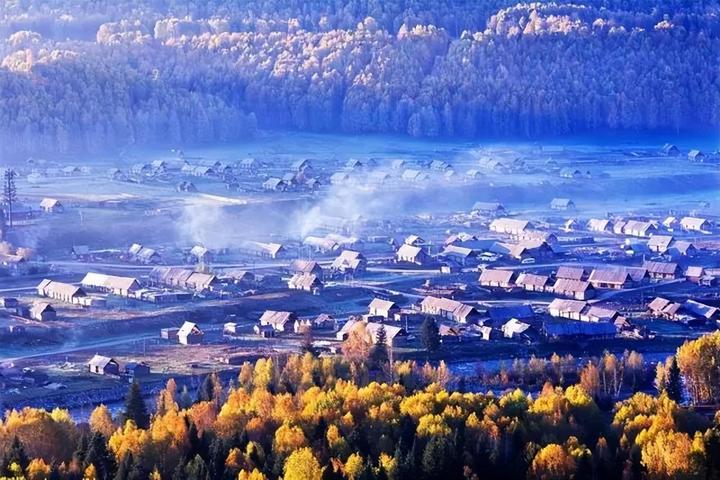
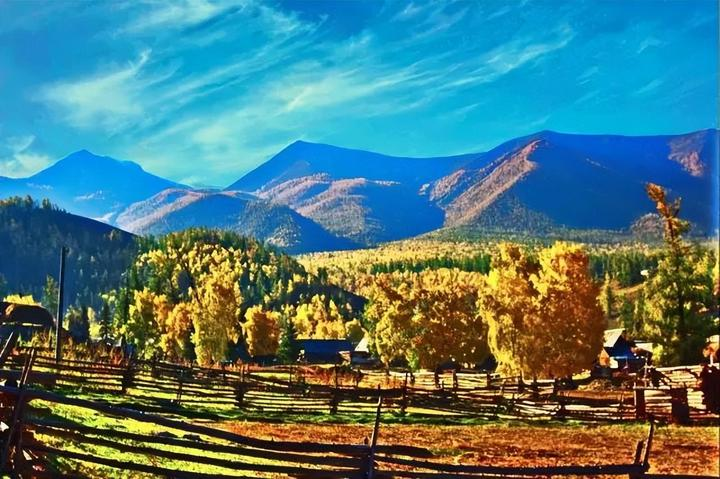
Day 3: Hemu Village, the most beautiful secluded village – Experience the traditional life of the Tuva people.
In autumn, the golden leaves of Hemu Village contrast beautifully with the rustic wooden houses. Walking along the village’s paths, the rustling of fallen leaves underfoot seems to whisper stories of the passing years. This is a great place to experience the life of the Tuva people. You can taste local delicacies, enjoy traditional singing and dancing, and immerse yourself in the charm of their unique culture.
Nestled in a vast open area surrounded by mountains, Hemu Village lies quietly, with the Tuva people’s pointed wooden houses and livestock pens scattered casually throughout the village.
A faint mist forms a winding white ribbon above the forest, drifting between the village and the mountains. The most captivating aspect of Hemu Village is its stunning autumn scenery, where mountains covered in red foliage are breathtaking. Smoke rises slowly through the autumn colors, forming a dreamy mist that makes the village look like a fairyland.
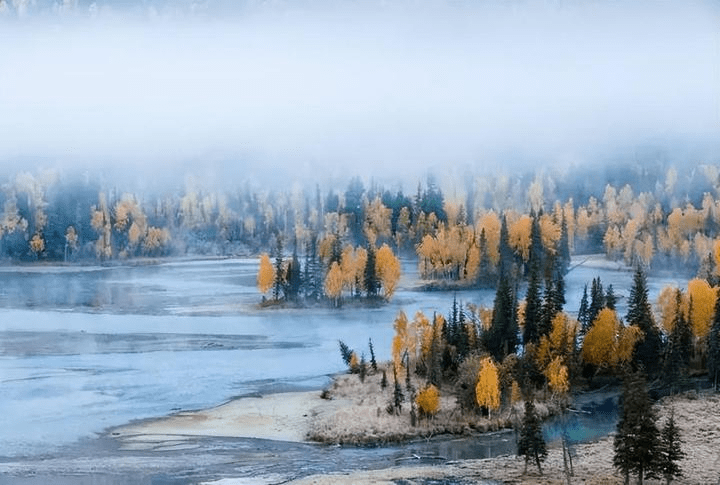
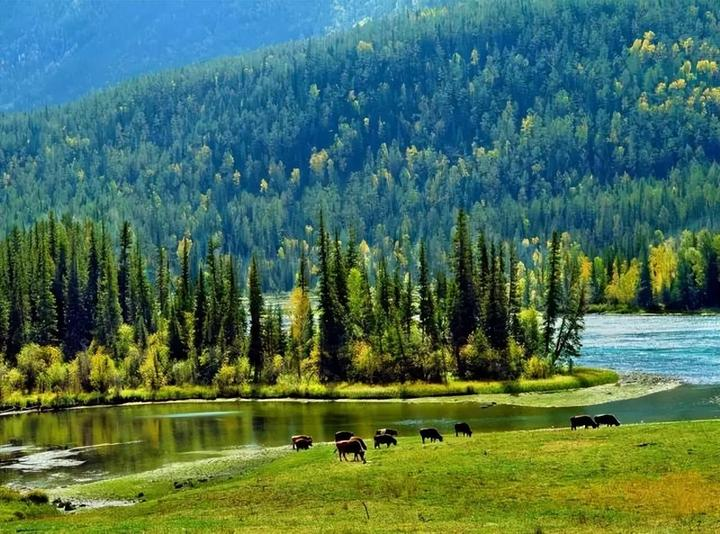
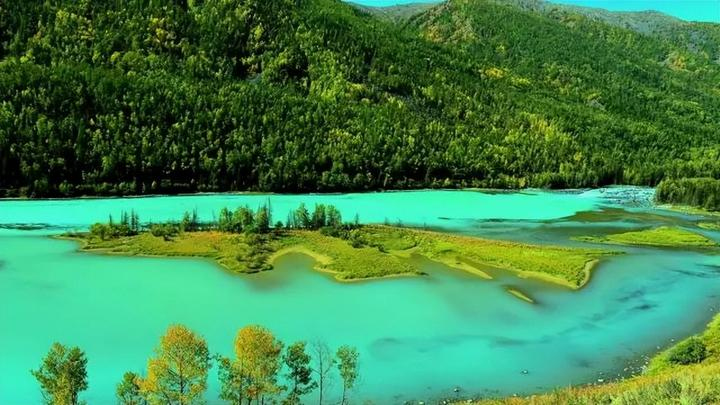
Day 4: Kanas – Immersing in the breathtaking scenery of lakes and mountains.
Kanas is one of the world’s rare “earthly paradises.” Its unparalleled beauty is something that even the best photography skills cannot fully capture.
Kanas combines the grandeur of northern landscapes with the delicate charm of southern waters. Additionally, there are other breathtaking spectacles such as the “Sea of Clouds with Buddha’s Light,” the “Color-Changing Lake,” the “Floating Wood Dyke,” and the “Lake Monster,” making it a true wonderland of the Western regions.
Kanas Lake: This lake, known as the “Earthly Fairyland,” reveals a unique charm in autumn. The lake’s water remains as emerald green as a gemstone, while the surrounding forests are transformed by autumn frost into a dazzling array of colors—fiery reds, golden yellows, and sunset oranges. These hues, set against the backdrop of a bright blue sky, form a breathtaking painting, as if nature itself had painted it with the finest brushstrokes.
Kanas Lake is an alpine lake nestled deep in the Altai Mountains’ dense forests. In 2009, it was named the “Most Beautiful Lake in China” by Chinese National Geography magazine.
Best time to visit: From June to early October.
Transportation: The Kanas Scenic Area has its own airport, and you can fly directly from Urumqi to Kanas. The flight takes about 50 minutes.
Day 5: From Baihaba to the Rainbow Beach, admire the colorful rocks and rivers.
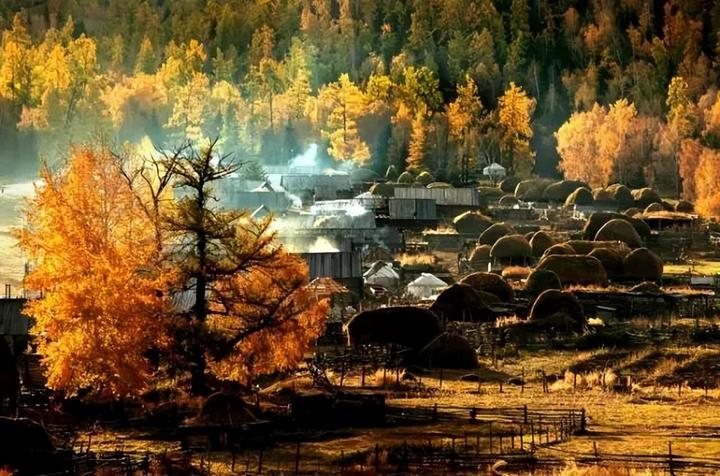
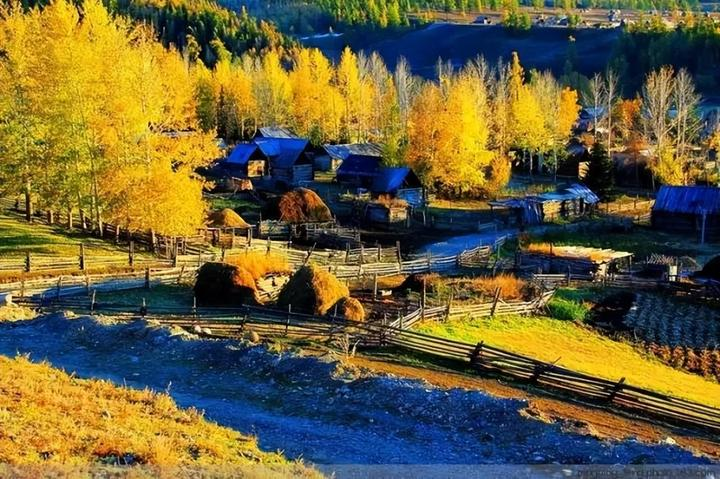
Baihaba Village, known as “the first village in the northwest,” faces the towering mountains of Kazakhstan in the distance. The dense golden pine forests of the Altai Mountains stretch all the way to Baihaba, where the villagers’ wooden houses and livestock pens are scattered harmoniously among the pine and birch forests, creating a peaceful and serene atmosphere. All of the village’s buildings are made of raw wood, with rustic log cabins as its signature feature, giving it the feel of a European-style village.
Baihaba Village: This place, known as “one of the eight most beautiful towns in China,” is especially breathtaking in autumn. The entire village is surrounded by golden birch forests, making it look like a golden fairy-tale world. The old wooden houses are scattered harmoniously among the trees, with smoke gently rising from the chimneys, creating a strong sense of rustic life.
At sunset and in the misty mornings, the smoke drifts lazily, while cows and sheep graze on the hills, painting a picture of harmony between humans and nature. If Kanas is a secluded, ancient paradise, then Baihaba is a fairy-tale world nestled in an untouched natural environment.
In the morning, immerse yourself in the rustic atmosphere on the grasslands of Baihaba. In the afternoon, head to the spectacular Rainbow Beach to admire Xinjiang’s most beautiful Yardang landforms. The hills here have unique geological features and display a variety of colors. At sunset, under the sunlight, the rocks primarily glow red, with shades of green, purple, yellow, white, black, and transitional hues, creating a vibrant and mesmerizing palette, which is why it’s called “Rainbow Beach.”
Whenever the wind blows, strange sounds of varying lengths and pitches echo from the gullies and beneath the rocks, adding a mysterious and otherworldly feel to the place.
Day 6: Keketohai – Enjoy the tranquility of lakes and forests.
Keketohai Town is located 48 kilometers northeast of Fuyun County in the Altai Mountains, in northern Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. In Kazakh, “Keketohai” means “green forest,” and in Mongolian, it means “blue river bend.”
In autumn, the golden birch forests of Keketohai beautifully complement the clear river waters. The river flows gently, reflecting the stunning scenery on both banks, like a giant mirror. Strolling along the river, feeling the breeze and listening to the birds sing, fills one with a sense of peace and serenity.
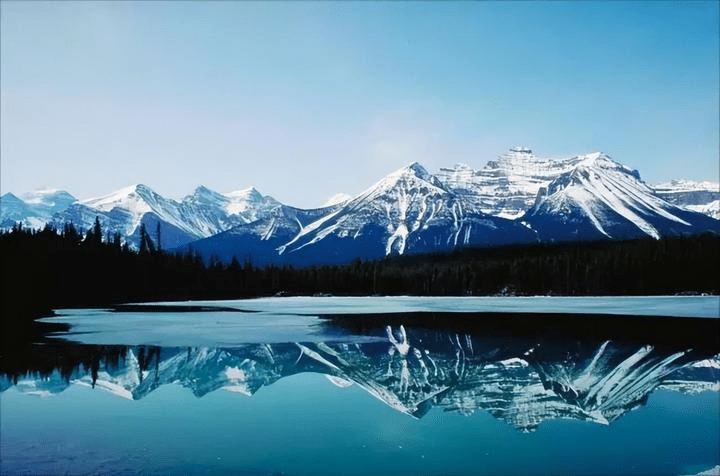
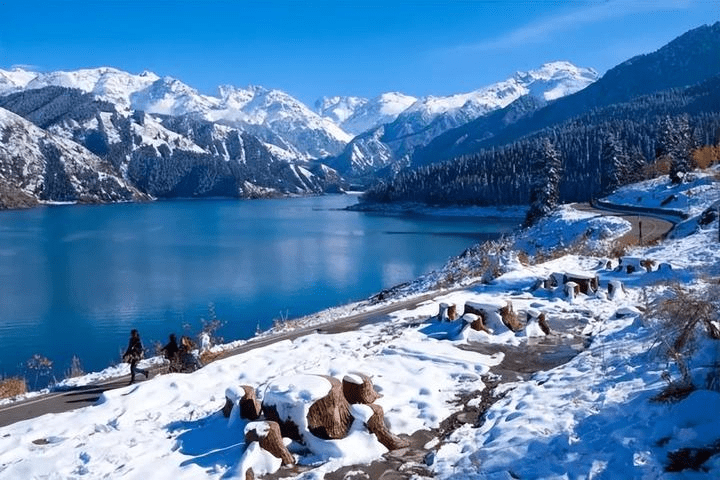
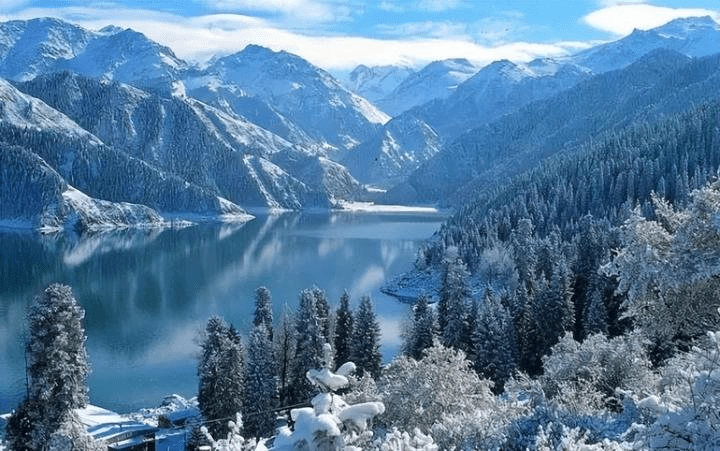
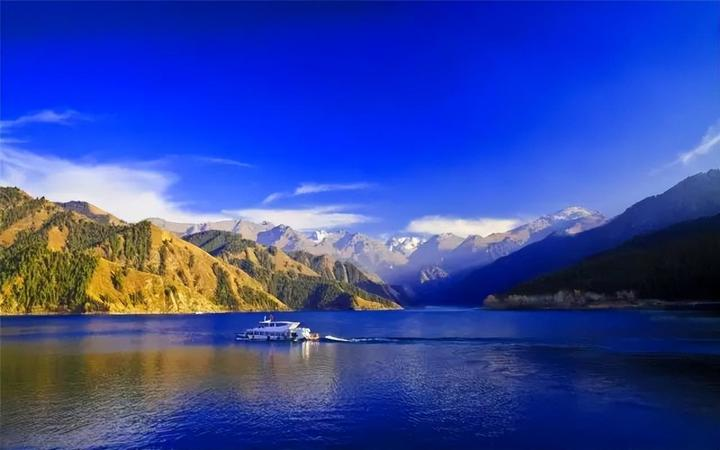
From here, you will have seen most of the beautiful autumn scenery in northern Xinjiang, and you can return to Urumqi to end your trip. If you have more time, you can visit Heavenly Lake (Tianchi) to admire the snowy mountains and emerald waters.
Heavenly Lake: A fairyland amidst the surrounding mountains.
Over the course of history, in the vast wilderness of China’s western regions, a place of extraordinary beauty emerged—Heavenly Lake in the Tianshan Mountains.
Historically known as “Jade Pool,” legend has it that King Mu of the Zhou dynasty traveled west and held a feast with the Queen Mother of the West here. In the Qing dynasty, during the reign of Emperor Qianlong, it was named “Tianchi,” meaning “Heavenly Mirror” or “Divine Lake.”
Heavenly Lake is an extraordinary and mesmerizing sacred site.
Its fame not only comes from the beautiful and mysterious legends associated with it throughout history, but also from its unique natural and cultural landscapes, renowned both domestically and internationally! The Bogda Peak of the Tianshan Mountains rises to 5,445 meters above sea level, its snow-covered glaciers extending throughout the year. The snowy mountains and the blue lake complement each other, creating breathtaking scenery. The surface of the lake is crescent-shaped, and the water is crystal clear, as pure as jade.
The snow-capped peaks reflect in the lake, surrounded by towering spruce trees, with the emerald waters as smooth as a mirror, forming a picturesque landscape. Encircled by mountains, the area is lush with green grass and vibrant wildflowers, earning it the title “Pearl of the Tianshan Mountains.” Tall, verdant spruce and pine trees cover the mountains and ridges, creating a dense forest canopy.
Link:https://peacelilysite.com/2024/10/18/xinjiangs-golden-tapestry-exploring-the-stunning-autumn-landscapes-of-chinas-northwest/
Source : photos from https://www.52hrtt.com/br/n/w/info/F1665986705929