The following article was published by the BBC News, Soutik Biswas, July 31, 2025:
Auction house Sotheby’s has returned a set of sacred jewels believed to be linked to the Buddha’s remains in India, after facing mounting pressure from the Indian government and global Buddhist leaders.
The Piprahwa Gems – described by archaeologists as one of the most astonishing finds of the modern era – were due to be auctioned in Hong Kong in May. But the sale was called off following diplomatic intervention and threats of legal action from Delhi.
The Mumbai-based conglomerate Godrej Industries Group has acquired the jewels, Sotheby’s said.
Sotheby’s said it was “delighted” to facilitate the return, following two months of negotiations involving the owner, the new buyer and the Indian government. The relics will now go on permanent public display in India, the auction house said.

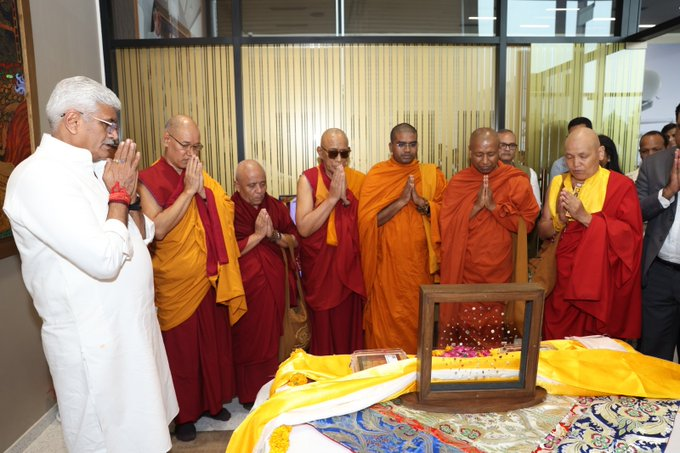
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the return on Wednesday, calling it a “proud and joyous moment” and a victory for the country’s cultural heritage. The relics, he said on X, were coming home after 127 years.
Godrej Industries Group, the buyer of the jewels, serves over 1.1 billion consumers worldwide across sectors including consumer goods, real estate, agriculture, finance, and chemicals, according to its website. Many of its products are household names in India.
“We are deeply honoured to contribute to this historic moment. The Piprahwa gems are not just artifacts – they are timeless symbols of peace, compassion, and the shared heritage of humanity,” Pirojsha Godrej, Executive Vice Chairperson of Godrej Industries Group, was quoted as saying in a government press statement.
Unearthed in 1898 by English estate manager William Claxton Peppé from a stupa in Piprahwa in northern India, near the Buddha’s birthplace, the cache included nearly 1,800 pearls, rubies, sapphires and gold sheets – buried alongside bone fragments identified by an inscribed urn as belonging to the Buddha himself.

Peppé eventually handed most of the gems, relics and reliquaries to the colonial Indian government: the bone relics went to the Buddhist King of Siam (Rama V). Five relic urns, a stone chest and most other relics were sent to the Indian Museum in Kolkata – then the Imperial Museum of Calcutta.

For over a century, the rest of the dazzling jewels remained largely hidden in a British private collection.
A set of 300 gems held by the Peppé family was publicly displayed at Sotheby’s Hong Kong in February and May. Over the past six years, the gems have appeared in major exhibitions, including The Met in 2023. The family has also launched a website to share their research.
Historians consider the relics the shared heritage of the Buddha’s Sakya clan and Buddhists worldwide. The bone fragments have since been distributed to countries like Thailand, Sri Lanka, and Myanmar, where they remain objects of veneration.

The planned sale of the Buddha relics by Sotheby’s in Hong Kong had sparked widespread ethical concerns, with scholars and Buddhist leaders questioning whether sacred objects – especially those linked to human remains – should be treated as commodities.
Critics challenged the seller’s authority to auction the relics, while defenders said a transparent sale was the fairest way to transfer custody. For many Buddhists, the jewels are inseparable from the sacred remains and meant to be venerated, not sold.
“Are the relics of the Buddha a commodity that can be treated like a work of art to be sold on the market?” Naman Ahuja, a Delhi-based art historian, had told the BBC in May. “And since they aren’t, how is the seller ethically authorised to auction them?
“Since the seller is termed the ‘custodian’, I would like to ask – custodian on whose behalf? Does custodianship permit them now to sell these relics?”
Chris Peppé, great-grandson of William, had told the BBC in May that the family looked into donating the relics, but all options presented problems and an auction seemed the “fairest and most transparent way to transfer these relics to Buddhists”.
He said that in all the monasteries he had visited “no Buddhists regard these as corporeal relics”.
“A few Buddhist academics at Western universities have recently offered a convoluted, fact-defying logic whereby they may be regarded as such. It’s an academic construct that is not shared by Buddhists in general who are familiar with the details of the find,” he said.
On 7 May, Sotheby’s postponed the auction of the jewels following media reports and concerns raised by the Indian government, citing the need for further discussions. A week later, it confirmed ongoing talks with India to find a mutually agreeable resolution.
This week, confirming the return of the jewels, Sotheby’s said it was “grateful to the Peppé family for having safeguarded the gems and for having worked with us – and with the Government of India – in good faith to achieve this historic outcome”.
Link:https://peacelilysite.com/2025/09/05/ancient-buddha-relics-returned-to-india/