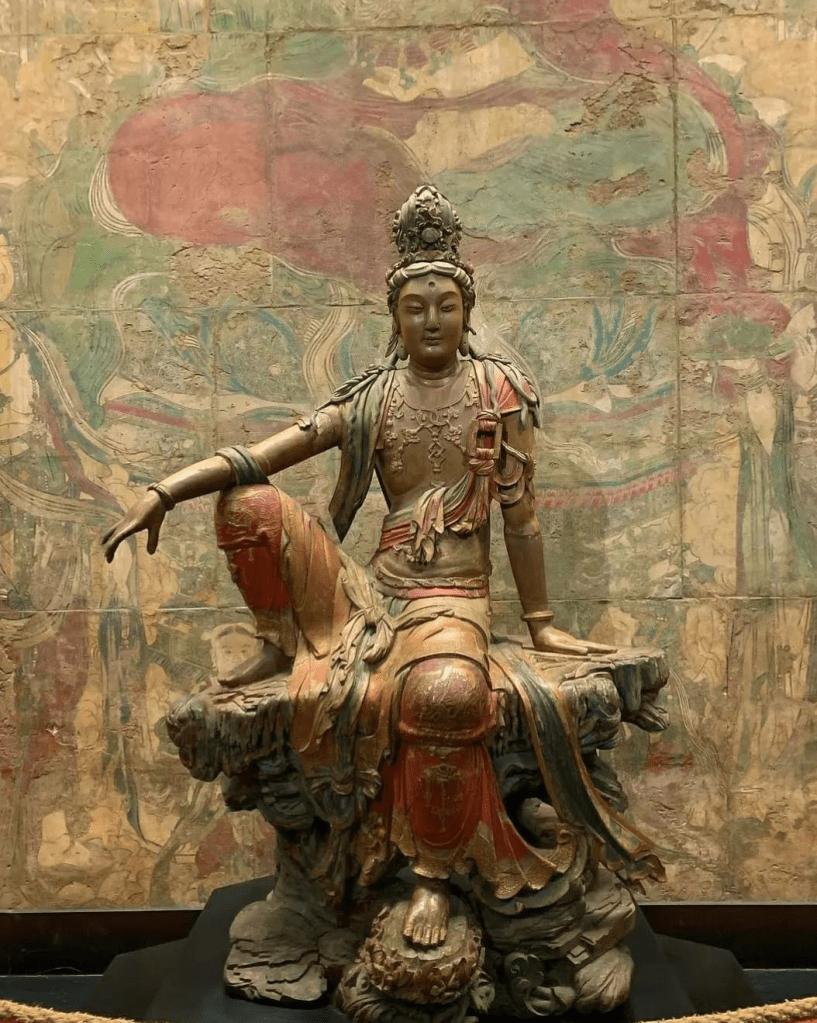
Tucked within the tranquil halls of the Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art stands a breathtaking wooden sculpture of Water-Moon Guanyin from the Liao Dynasty—a work hailed as “the most magnificent surviving sculpture in China” and “a triumph of religion and aesthetics.” It has also been honored by the media as “one of the thirty finest works held in American public institutions.”
Officially labeled by the museum as “Guanyin of the Southern Sea,” this statue rises to an impressive height of 2.4 meters. Aside from the right forearm, the entire figure—including its base—was masterfully carved from a single block of wood. Dating back to the 11th or 12th century (Liao or Jin Dynasty), the sculpture has been remarkably well-preserved over the centuries.
This Guanyin is an extraordinary example of religious artistry. Her face is gently sculpted with refined features—serene, graceful, and quietly majestic. Adorned with a jeweled crown, her eyes are softly closed, gazing downward in meditation and compassion. The statue’s pose reflects the elegance and wisdom traditionally associated with the feminine form, especially in the flowing hand gestures—while still retaining some subtle masculine traits in the upper body, a nod to Guanyin’s transcendent nature.
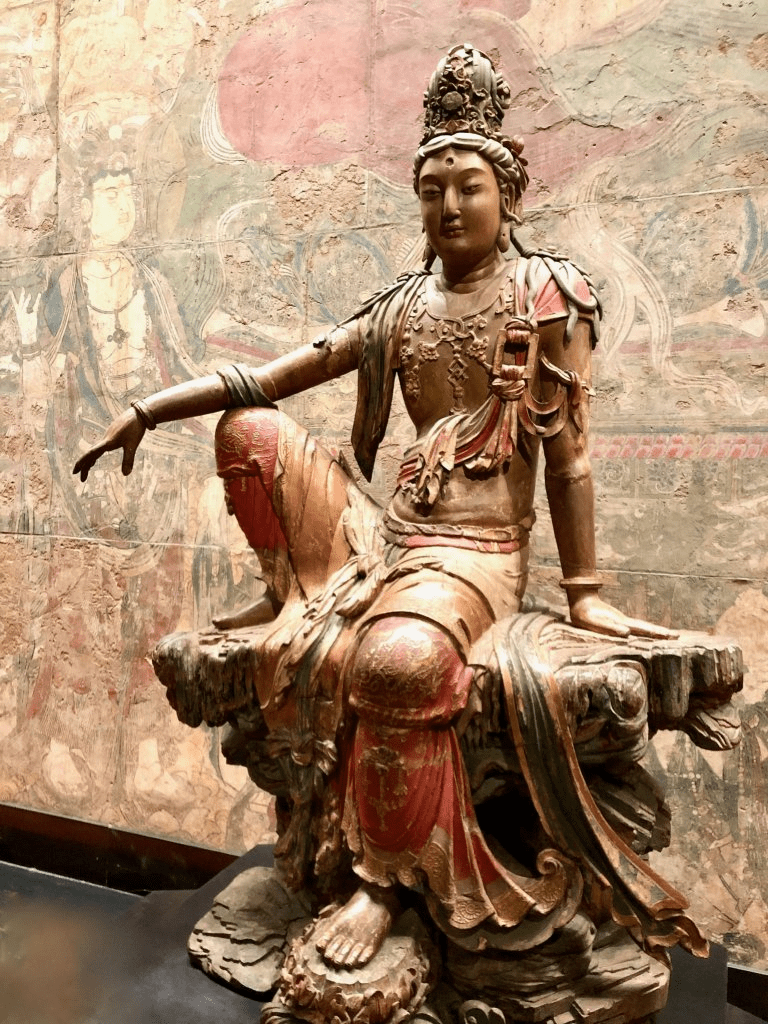
In classic iconography, Water-Moon Guanyin is often portrayed seated on a rock or lotus throne, gazing compassionately at the world. In this sculpture, she sits with one leg bent and the other gracefully draped downward. Her right arm rests lightly on her knee, fingers gently curved, as she gazes diagonally downward with a calm smile—evoking the image of the moon reflected in water. This visual metaphor powerfully symbolizes a core Buddhist teaching: the illusion of form and the essence of emptiness.
Every aspect of the statue—the proportions, the flowing posture, the tranquil expression—conveys a sense of effortless grace, inner freedom, and compassionate presence. It is a piece that invites quiet reflection, stirring something deep within the soul of the viewer.
The Legend Behind the Water-Moon Guanyin
The form of Water-Moon Guanyin, also known as “Auspicious Water Guanyin” or “Auspicious Water Bodhisattva,” is one of the most beloved among the thirty-three manifestations of Guanyin in Chinese Buddhist tradition. Interestingly, the name “Water-Moon” does not come from early Buddhist scriptures, but rather from Chinese folklore—born of the fusion between Buddhism and indigenous Chinese culture.
According to legend, Guanyin once appeared in Suzhou during a time of war, where she witnessed the brutal slaughter of civilians by the Jin army. Out of great compassion, she transformed into a beautiful woman, built a ritual platform, and began chanting sutras to deliver the souls of the dead. When her recitation was complete, someone among the crowd recognized her divine aura and asked to see her true form.
The Bodhisattva pointed to the riverbank. There, reflected in the still waters, was the image of a radiant full moon, within which her sacred figure appeared—graceful and ethereal. Among the witnesses was a talented artist named Qiu Zijing, who quickly sketched the vision. As his painting circulated, this image came to be known and venerated as the Water-Moon Guanyin.
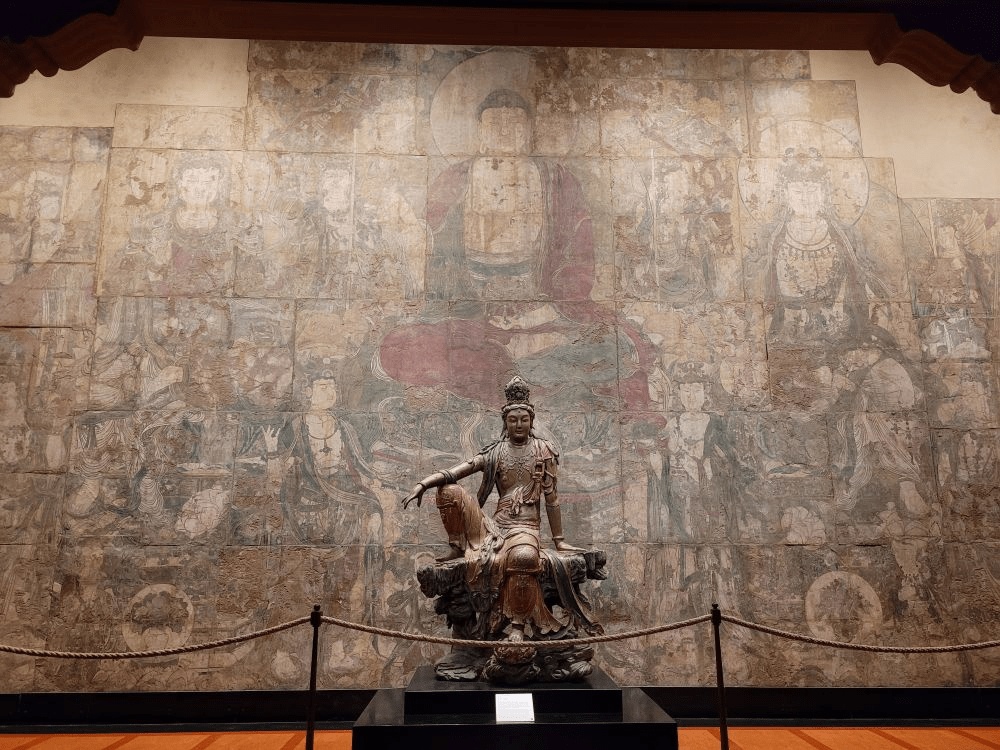
A Space Worthy of the Divine
To properly honor this extraordinary statue, the Nelson-Atkins Museum created an expansive Chinese Temple Gallery. Behind Guanyin stands a Yuan Dynasty mural titled “Assembly of the Radiant Buddha,” originally from Guangsheng Temple in Shanxi Province. Above hangs a carved Ming Dynasty coffered ceiling adorned with dragons, while in front, finely carved lattice doors from a Qing Dynasty official’s residence in Beijing complete the immersive setting.
This harmonious environment allows visitors to experience the sculpture not just as a museum piece, but as a living expression of faith, beauty, and timeless spiritual insight.
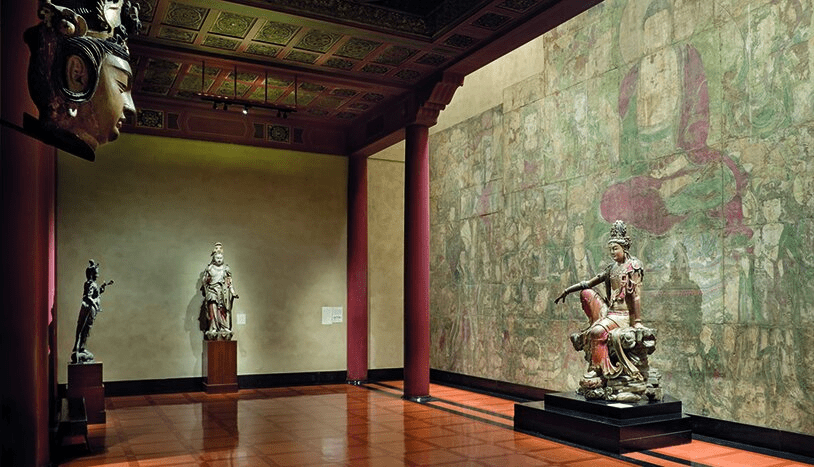


The Water-Moon Guanyin at the Nelson-Atkins Museum is more than an ancient sculpture—it is a sacred embodiment of compassion, artistry, and transcultural storytelling. Whether viewed through the lens of religion, history, or aesthetics, it stands as a serene reminder of the enduring power of beauty to transcend time and touch the human spirit.